Java - Arrays
Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable. In Java, all elements of an array must be of same datatype.
Create an Array
It starts with defining the datatype of the array with enclosed in square brackets [ ], followed by name of the array.
Initialize an Array
An array can be initialized by separating it's elements by comma , and enclosing with curly brackets { }. Please note that declaration of an array does not allocate memory for the array. To allocate the memory for an array, it must be initialized. If the array is not initialized at the time of declaration it must be initialized with new keyword followed by datatype and size of array enclosed in square bracket [ ]. See the syntax below for various methods of declaration and initialization.
Syntax
//both declaration methods are valid in Java
int[] MyArray;
int MyArray[];
//declaration and initialization of
//an integer array separately
int[] MyArray;
MyArray = new int[5]; //size of array is 5
MyArray[0] = 10; //first element is 10.
//declaration and initialization of an string
//array in a single line
String[] MyArray = {"MON", "TUE", "WED"};
//Another method of declaration and initialization
//of an string array in a single line
String[] MyArray = new String[5];
Access element of an Array
An element of an array can be accessed with it's index number. In Java, the index number of an array starts with 0 as shown in the figure below:
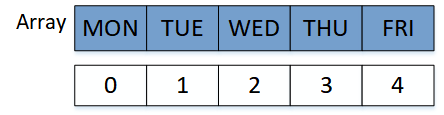
The example below describes how to access elements of an array using its index number.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating an array with 5 elements
String[] weekday = {"MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI"};
//accessing the element with index number 4
System.out.println(weekday[4]);
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
FRI
Modify elements of an Array
Any element of an Array can be changed using its index number and assigning a new value.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] weekday = {"MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI"};
weekday[0] = "MON_new";
weekday[3] = "THU_new";
System.out.println(weekday[0]);
System.out.println(weekday[3]);
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
MON_new THU_new
Number of elements in Array
Number of elements in an array can be estimated using length property of the array.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] weekday = {"MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI"};
System.out.println(weekday.length);
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
5
Loop over an Array
With for loop or while loop, we can access each elements of an Array. Along with this, we can also use for-each loop, which is available only for loop through the elements of array.
For Loop over an Array
In the example below, for loop is used to access all elements of the given array.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] weekday = {"MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI"};
for(int i = 0; i < weekday.length; i++) {
System.out.println(weekday[i]);
}
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
MON TUE WED THU FRI
While Loop over an Array
Similarly, while loop is also be used to access elements of the array.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int i = 0;
while(i < numbers.length) {
System.out.println(numbers[i]);
i++;
}
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
10 20 30 40 50
For-each over an Array
Syntax
for(datatype i : MyArray){
statements;
}
In the example below, for-each loop is used to access all elements of the given array.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for ( int i : numbers) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
10 20 30 40 50
Multi-dimensional Array
Multi-dimensional array can be viewed as arrays of arrays. Java allows you to define array of any dimension. For-loop or While-loop can be used to access elements of a multi-dimensional arrays.
Syntax
//2-dimension array
int[][] MyArray;
//3-dimension array
int[][][] MyArray;
//2-dimensional array
int[][] MyArray = {{10,20,30},{100,200}};
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] numbers = {{10, 20, 30}, {40, 50, 60}};
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.println(numbers[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
The output of the above code will be:
10 20 30 40 50 60


