C++ <vector> - crbegin() Function
The C++ vector::crbegin function returns the constant reverse iterator (const_reverse_iterator) pointing to the last element of the vector. Please note that, Unlike the vector::back function, which returns a direct reference to the last element, it returns the const_reverse_iterator pointing to the same element of the vector.
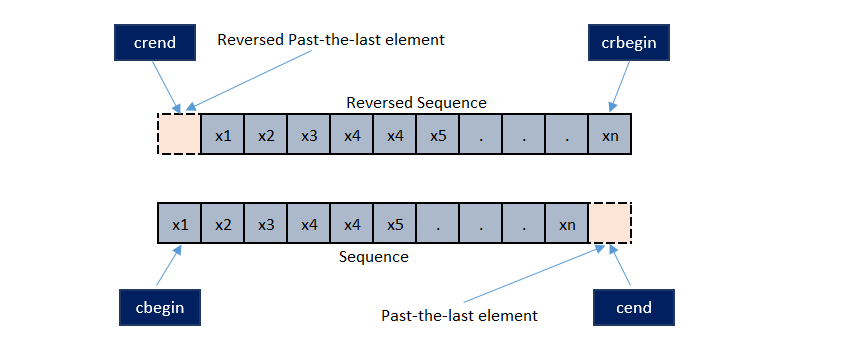
Note: A const_reverse_iterator is an iterator that points to constant value and iterates in backward direction. Increasing a const_reverse_iterator results into moving to the beginning of the vector container and decreasing it results into moving to the end of the vector container. Along with this, it cannot be used to modify the contents it points to, even if the vector element is not itself constant.
Syntax
const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const noexcept;
Parameters
No parameter is required.
Return Value
A const_reverse_iterator to the reverse beginning of the sequence container.
Time Complexity
Constant i.e, Θ(1).
Example:
In the example below, the vector::crbegin function returns the const_reverse_iterator pointing to the last element of the vector MyVector.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main (){
vector<string> MyVector{"Alpha","Coding","Skills"};
vector<string>::const_reverse_iterator crit;
crit = MyVector.crbegin();
cout<<*crit<<" ";
crit++;
cout<<*crit<<" ";
crit++;
cout<<*crit<<" ";
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
Skills Coding Alpha
Example:
Lets see another example where the vector called MyVector contains integer values and vector::crbegin function is used with vector::crend function to specify a range including all elements of the vector container.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main (){
vector<int> MyVector{10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
vector<int>::const_reverse_iterator crit;
for(crit = MyVector.crbegin(); crit != MyVector.crend(); ++crit)
cout<<*crit<<" ";
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
50 40 30 20 10
❮ C++ <vector> Library


