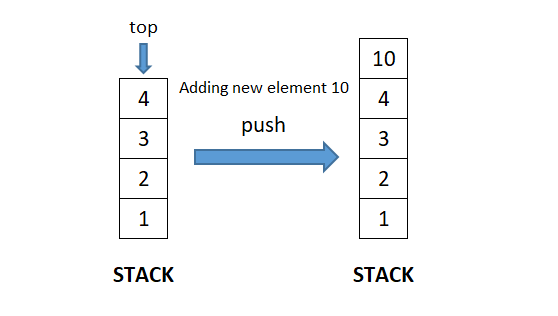
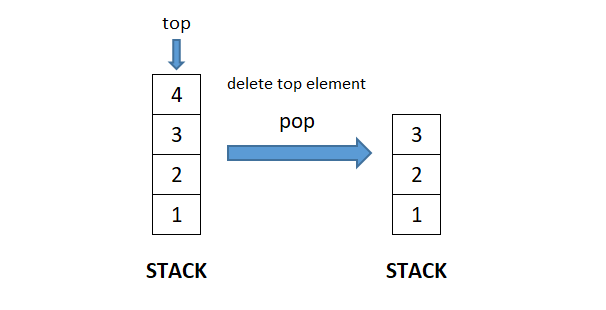
Data Structure - Stack
A stack is a linear dynamic data structure that follows Last-In/First-Out (LIFO) principle. In a stack, addition of a new element and deletion of an element occurs at the same end which implies that the element which is added last in the stack will be the first to be removed from the stack.
Features of stack
- It is a dynamic data structure.
- It has dynamic size.
- It uses dynamic memory allocation.
Basic Operations of a Stack
- isEmpty(): Checks whether the stack is empty or not.
- size(): Returns the size of the stack.
- topElement(): Returns the top element of the stack.
- push(x): Adds a new element ‘x’ at the top of the stack. Consequently, size of the stack increases by 1.
- pop(): Deletes the top element of the stack. Consequently, size of the stack decreases by 1.
Implementation of Stack
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
class CreateStack {
int top;
public:
//assigning MAX size of the stack
int stack[MAX];
CreateStack() {
top = -1;
}
void isEmpty();
int size();
void push(int x);
void pop();
int topElement();
};
// create a function to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
void CreateStack::isEmpty() {
if(top == -1) {
cout<<"Stack is empty."<<"\n";
} else {
cout<<"Stack is not empty."<<"\n";
}
}
//create a function to return size of the stack
int CreateStack::size() {
return top+1;
}
//create a function to add new element
void CreateStack::push(int x){
if(top == (MAX - 1)){
cout<<"Stack size limit reached."<<"\n";
} else {
stack[++top] = x;
cout<<x<<" is added into the stack."<<"\n";
}
}
//create a function to delete top element
void CreateStack::pop() {
if(top < 0){
cout<<"Stack is empty."<<"\n";
} else {
int x = stack[top--];
cout<<x<<" is deleted from the stack."<<"\n";
}
}
//create a function to get top element
int CreateStack::topElement() {
if(top < 0) {
cout<<"Stack is empty."<<"\n";
return 0;
} else {
return stack[top];
}
}
// test the code
int main() {
class CreateStack MyStack;
MyStack.push(10);
MyStack.push(20);
MyStack.push(30);
MyStack.push(40);
MyStack.pop();
MyStack.isEmpty();
return 0;
}
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 100
//define structure of a stack
struct stack {
int array[MAX];
int top;
};
typedef struct stack stk;
void CreateStack(stk *s) {
s->top = -1;
}
// create a function to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
void isEmpty(stk *s) {
if(s->top == -1) {
printf("Stack is empty.\n");
} else {
printf("Stack is not empty.\n");
}
}
//create a function to return size of the stack
int size(stk *s) {
return s->top+1;
}
//create a function to add new element
void push(stk *s, int x) {
if(s->top == (MAX - 1)) {
printf("Stack size limit reached.\n");
} else {
s->array[++s->top] = x;
printf("%i is added into the stack.\n", x);
}
}
//create a function to delete top element
void pop(stk *s){
if(s->top < 0){
printf("Stack is empty.\n");
} else {
int x = s->array[s->top--];
printf("%i is deleted from the stack.\n", x);
}
}
//create a function to get top element
int topElement(stk *s) {
if(s->top < 0) {
printf("Stack is empty.\n");
return 0;
} else {
return s->array[s->top];
}
}
// test the code
int main() {
stk s;
stk *MyStack;
MyStack = &s;
CreateStack(MyStack);
push(MyStack, 10);
push(MyStack, 20);
push(MyStack, 30);
push(MyStack, 40);
pop(MyStack);
isEmpty(MyStack);
return 0;
}
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
# function to create stack
def CreateStack():
stack = []
return stack
# create function to check whether
# the stack is empty or not
def isEmpty(stack):
if(len(stack) == 0):
print("Stack is empty.")
else:
print("Stack is not empty.")
#create function to return size of the stack
def size(stack):
return len(stack)
#create function to add new element
def push(stack, newElement):
stack.append(newElement)
print(newElement, "is added into the stack.")
#create function to delete top element
def pop(stack):
print(stack.pop(), "is deleted from the stack.")
#create function to get top element
def topElement(stack):
return stack[len(stack) - 1]
# test the code
MyStack = CreateStack()
push(MyStack, 10)
push(MyStack, 20)
push(MyStack, 30)
push(MyStack, 40)
pop(MyStack)
isEmpty(MyStack)
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
class CreateStack {
static final int MAX = 100;
int top;
//assigning MAX size of the stack
int stack[] = new int[MAX];
CreateStack() {
top = -1;
}
// create a method to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
void isEmpty() {
if(top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is not empty.");
}
}
//create a method to return size of the stack
int size() {
return top+1;
}
//create a method to add new element
void push(int x){
if(top == (MAX - 1)){
System.out.println("Stack size limit reached.");
} else {
stack[++top] = x;
System.out.println(x + " is added into the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to delete top element
void pop(){
if(top < 0){
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
int x = stack[top--];
System.out.println(x + " is deleted from the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to get top element
int topElement() {
if(top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
return 0;
} else {
return stack[top];
}
}
}
// test the code
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateStack MyStack = new CreateStack();
MyStack.push(10);
MyStack.push(20);
MyStack.push(30);
MyStack.push(40);
MyStack.pop();
MyStack.isEmpty();
}
}
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
using System;
class CreateStack {
private int MAX = 100;
private int top;
private int[] stack;
public CreateStack() {
//assigning MAX size of the stack
stack = new int[MAX];
top = -1;
}
// create a method to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
public void isEmpty() {
if(top == -1) {
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty.");
} else {
Console.WriteLine("Stack is not empty.");
}
}
//create a method to return size of the stack
public int size() {
return top+1;
}
//create a method to add new element
public void push(int x){
if(top == (MAX - 1)){
Console.WriteLine("Stack size limit reached.");
} else {
stack[++top] = x;
Console.WriteLine(x + " is added into the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to delete top element
public void pop(){
if(top < 0){
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty.");
} else {
int x = stack[top--];
Console.WriteLine(x + " is deleted from the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to get top element
public int topElement() {
if(top < 0) {
Console.WriteLine("Stack is empty.");
return 0;
} else {
return stack[top];
}
}
}
// test the code
class MyProgram {
static void Main(string[] args) {
CreateStack MyStack = new CreateStack();
MyStack.push(10);
MyStack.push(20);
MyStack.push(30);
MyStack.push(40);
MyStack.pop();
MyStack.isEmpty();
}
}
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
<?php
class CreateStack {
public $top;
public $stack = array();
function __construct() {
$this->top = -1;
}
// create a function to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
public function isEmpty() {
if($this->top == -1) {
echo "Stack is empty. \n";
} else {
echo "Stack is not empty. \n";
}
}
//create a function to return size of the stack
public function size() {
return $this->top+1;
}
//create a function to add new element
public function push($x) {
$this->stack[++$this->top] = $x;
echo $x." is added into the stack. \n";
}
//create a function to delete top element
public function pop() {
if($this->top < 0){
echo "Stack is empty. \n";
} else {
$x = $this->stack[$this->top--];
echo $x." is deleted from the stack. \n";
}
}
public function topElement() {
if($this->top < 0) {
echo "Stack is empty. \n";
} else {
return $this->stack[$this->top];
}
}
}
// test the code
$MyStack = new CreateStack();
$MyStack->push(10);
$MyStack->push(20);
$MyStack->push(30);
$MyStack->push(40);
$MyStack->pop();
$MyStack->isEmpty();
?>
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.