MySQLi - Using Joins
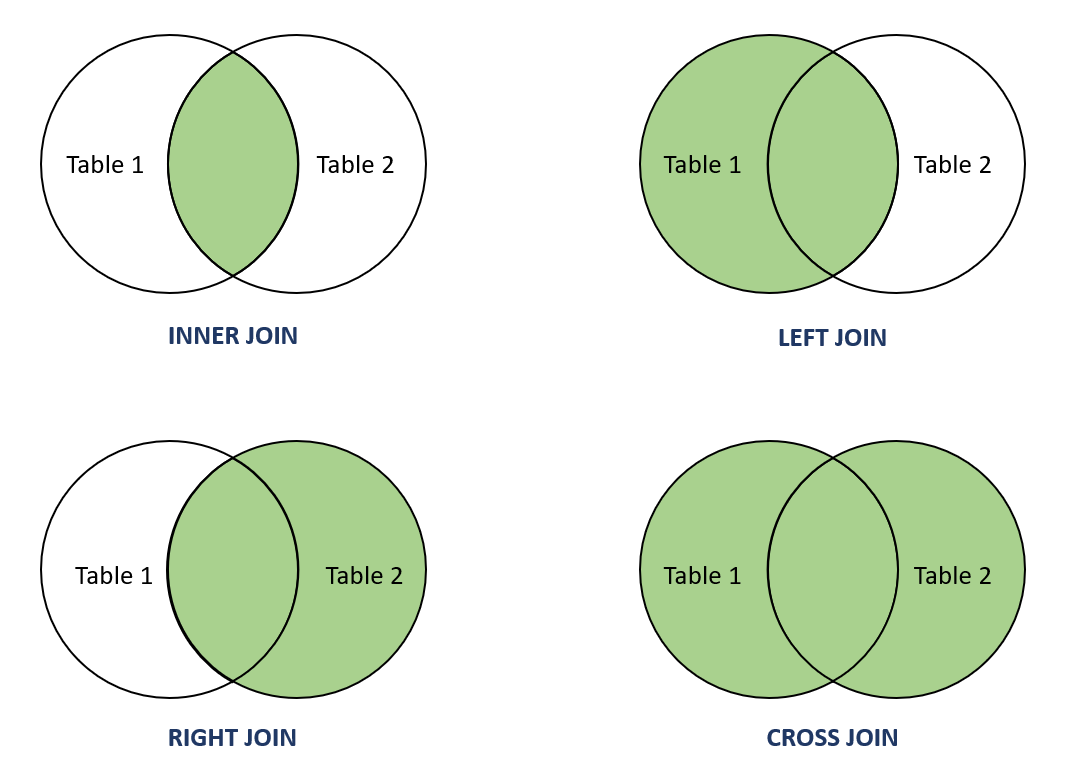
The MySQL JOIN clause is used to combine rows of two or more tables based on common column between them. There are four types of JOINs in MySQL:
- INNER JOIN - It is sometimes called simple JOIN. It returns records based on matching rows in both tables.
- LEFT JOIN - It is sometimes called LEFT OUTER JOIN. It returns records which contains all rows from left table and matching rows from right tables.
- RIGHT JOIN - It is sometimes called RIGHT OUTER JOIN. It returns records which contains all rows from right table and matching rows from left tables.
- CROSS JOIN - Returns records which contains all rows from both tables. It is sometimes called CARTESIAN JOIN because in the absence of a WHERE condition it behaves like a CARTESIAN PRODUCT i.e., the number of rows in the result-set is the product of the number of rows of the two tables.
Consider a database containing tables called Employee and Contact_Info with the following records:
Table 1: Employee table
| EmpID | Name | City | Age | Salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | London | 25 | 3000 |
| 2 | Marry | New York | 24 | 2750 |
| 3 | Jo | Paris | 27 | 2800 |
| 4 | Kim | Amsterdam | 30 | 3100 |
| 5 | Ramesh | New Delhi | 28 | 3000 |
| 6 | Huang | Beijing | 28 | 2800 |
Table 2: Contact_Info table
| Phone_Number | EmpID | Address | Gender |
|---|---|---|---|
| +1-8054098000 | 2 | Brooklyn, New York, USA | F |
| +33-147996101 | 3 | Grenelle, Paris, France | M |
| +31-201150319 | 4 | Geuzenveld, Amsterdam, Netherlands | F |
| +86-1099732458 | 6 | Yizhuangzhen, Beijing, China | M |
| +65-67234824 | 7 | Yishun, Singapore | M |
| +81-357799072 | 8 | Koto City, Tokyo, Japan | M |
In the query below, the INNER JOIN clause is used with Employee and Contact_Info tables based on common column EmpID. It returns Name, Age and Address columns based on match found in both tables.
SELECT Employee.Name, Employee.Age, Contact_Info.Address FROM Employee INNER JOIN Contact_Info ON Employee.EmpID = Contact_Info.EmpID;
This will produce the result as shown below:
| Name | Age | Address |
|---|---|---|
| Marry | 24 | Brooklyn, New York, USA |
| Jo | 27 | Grenelle, Paris, France |
| Kim | 30 | Geuzenveld, Amsterdam, Netherlands |
| Huang | 28 | Yizhuangzhen, Beijing, China |
Please note that, to connect to the MySQL server, mysqli_connect() function can be used. After establishing the connection, mysqli_query() function can be used to perform a query on the database.
The num_rows() function can be used to check if there are more than zero rows returned. Then, the fetch_assoc() function can be used to fetch the result set as an associative array. Later on the free_result() function can be used to free the memory associated with the result.
MySQL JOIN - Object-oriented style
The example below demonstrates how to perform INNER JOIN discussed above using object-oriented style.
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDatabase";
//establishing connection
$mysqli = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
//checking connection
if ($mysqli->connect_errno) {
echo "Failed to connect to MySQL: ". $mysqli->connect_error;
exit();
}
//getting query result from the database
$sql = 'SELECT Employee.Name, Employee.Age, Contact_Info.Address
FROM Employee
INNER JOIN Contact_Info
ON Employee.EmpID = Contact_Info.EmpID;';
$result = $mysqli->query($sql);
//fetching associative array
while ($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
printf("Name: %s, Age: %d, Address: %s\n",
$row["Name"], $row["Age"], $row["Address"]);
}
//free result set
$result->free_result();
//closing the connection
$mysqli->close();
?>
The output of the above code will be:
Name: Marry, Age: 24, Address: Brooklyn, New York, USA Name: Jo, Age: 27, Address: Grenelle, Paris, France Name: Kim, Age: 30, Address: Geuzenveld, Amsterdam, Netherlands Name: Huang, Age: 28, Address: Yizhuangzhen, Beijing, China
MySQL JOIN - Procedural style
To obtain the same result using procedural style, the following script can be used.
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDatabase";
//establishing connection
$mysqli = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
//checking connection
if (mysqli_connect_errno()) {
echo "Failed to connect to MySQL: ". mysqli_connect_error();
exit();
}
//getting query result from the database
$sql = 'SELECT Employee.Name, Employee.Age, Contact_Info.Address
FROM Employee
INNER JOIN Contact_Info
ON Employee.EmpID = Contact_Info.EmpID;';
$result = mysqli_query($mysqli, $sql);
//fetching associative array
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)) {
printf("Name: %s, Age: %d, Address: %s\n",
$row["Name"], $row["Age"], $row["Address"]);
}
//free result set
mysqli_free_result($result);
//closing the connection
mysqli_close($mysqli);
?>
The output of the above code will be:
Name: Marry, Age: 24, Address: Brooklyn, New York, USA Name: Jo, Age: 27, Address: Grenelle, Paris, France Name: Kim, Age: 30, Address: Geuzenveld, Amsterdam, Netherlands Name: Huang, Age: 28, Address: Yizhuangzhen, Beijing, China
Complete MySQLi Reference
For a complete reference of all properties, methods and functions of PHP MySQLi extension, see MySQLi Reference.


