Merge Sort
Merge sort is a divide and conquer algorithm. It is based on the idea of dividing the unsorted array into several sub-array until each sub-array consists of a single element and merging those sub-array in such a way that results into a sorted array. The process step of merge sort can be summarized as follows:
- Divide: Divide the unsorted array into several sub-array until each sub-array contains only single element.
- Merge: Merge the sub-arrays in such way that results into sorted array and merge until achieves the original array.
- Merging technique: the first element of the two sub-arrays is considered and compared. For ascending order sorting, the element with smaller value is taken from the sub-array and becomes a new element of the sorted array. This process is repeated until both sub-array are emptied and the merged array becomes sorted array.
Example:
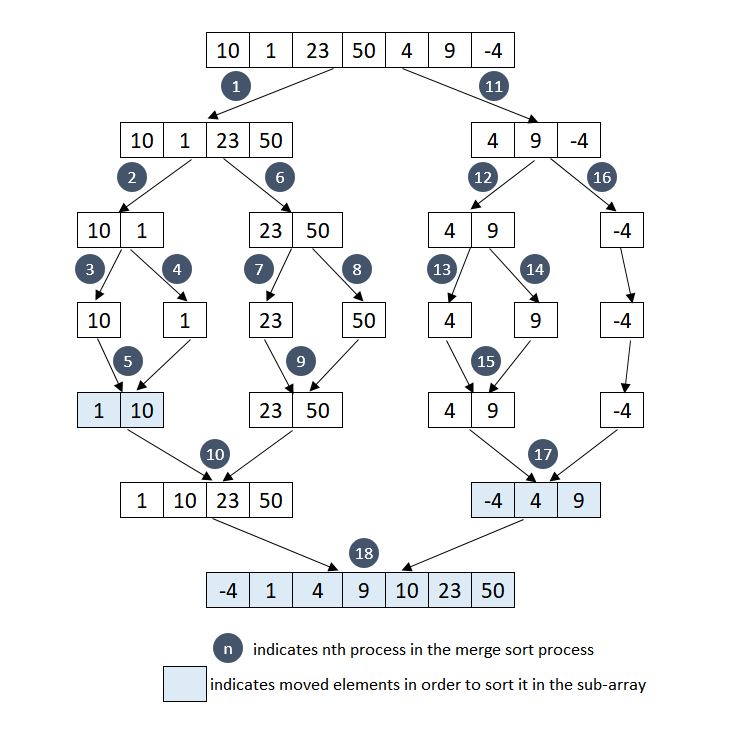
To understand the merge sort, lets consider an unsorted array [4, 9, -4] (right side array created after 11th process in the below diagram) and discuss each step taken to sort the array in ascending order.
At the first step, the array [4, 9, -4] is divided into two sub-array. The first sub-array contains [4, 9] and second sub-array contains [-4]. As the number of element in the first sub-array is greater than one, it is further divided into sub-arrays consisting of elements [4] and [9] respectively. As the number of elements in all sub-arrays is one, hence the further dividing of the array can not be done.
In the merging process, The sub-arrays formed in the last step are combined together using the process mentioned above to form a sorted array. First, [4] and [9] sub-arrays are merged together to form a sorted sub-array [4, 9]. Then [4, 9] and [-4] sub-arrays are merged together to form final sorted array [-4, 4, 9]
Implementation of Merge Sort
# function for merge sort - splits the MyList
# and call merge function to sort and merge the MyList
# mergesort is a recursive function
def mergesort(MyList, left, right):
if left < right:
mid = left + (right - left)//2
mergesort(MyList, left, mid)
mergesort(MyList, mid+1, right)
merge(MyList, left, mid, right)
# merge function performs sort and merge operations
# for mergesort function
def merge(MyList, left, mid, right):
# Create two temporary List to hold split
# elements of main MyList
n1 = mid - left + 1 # no of elements in LeftList
n2 = right - mid # no of elements in RightList
LeftList = MyList[left:mid+1]
RightList = MyList[mid+1:right+1]
# In below section x, y and z represents index number
# of LeftList, RightList and MyList respectively
x, y, z = 0, 0, left
while x < n1 and y < n2:
if LeftList[x] < RightList[y]:
MyList[z] = LeftList[x]
x+=1
else:
MyList[z] = RightList[y]
y+=1
z+=1
# Copying the remaining elements of LeftList
while x < n1:
MyList[z] = LeftList[x]
x+=1
z+=1
# Copying the remaining elements of RightList
while y < n2:
MyList[z] = RightList[y]
y+=1
z+=1
# function to print list
def PrintList(MyList):
for i in MyList:
print(i, end=" ")
print("\n")
# test the code
MyList = [10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4]
n = len(MyList)
print("Original List")
PrintList(MyList)
mergesort(MyList, 0, n-1)
print("Sorted List")
PrintList(MyList)
The above code will give the following output:
Original List 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted List -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
public class MyClass {
// function for merge sort - splits the array
// and call merge function to sort and merge the array
// mergesort is a recursive function
static void mergesort(int Array[], int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
mergesort(Array, left, mid);
mergesort(Array, mid+1, right);
merge(Array, left, mid, right);
}
}
// merge function performs sort and merge operations
// for mergesort function
static void merge(int Array[], int left, int mid, int right) {
// Create two temporary array to hold split
// elements of main array
int n1 = mid - left + 1; //no of elements in LeftArray
int n2 = right - mid; //no of elements in RightArray
int LeftArray[] = new int[n1];
int[] RightArray = new int [n2];
for(int i=0; i < n1; i++) {
LeftArray[i] = Array[left + i];
}
for(int i=0; i < n2; i++) {
RightArray[i] = Array[mid + i + 1];
}
// In below section x, y and z represents index number
// of LeftArray, RightArray and Array respectively
int x=0, y=0, z=left;
while(x < n1 && y < n2) {
if(LeftArray[x] < RightArray[y]) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
}
else {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
}
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of LeftArray
while(x < n1) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of RightArray
while(y < n2) {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
z++;
}
}
// function to print array
static void PrintArray(int Array[]) {
int n = Array.length;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
System.out.print(Array[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// test the code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] MyArray = {10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4};
int n = MyArray.length;
System.out.println("Original Array");
PrintArray(MyArray);
mergesort(MyArray, 0, n-1);
System.out.println("\nSorted Array");
PrintArray(MyArray);
}
}
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
static void mergesort(int Array[], int left, int right);
static void merge(int Array[], int left, int mid, int right);
static void PrintArray(int Array[], int n);
// function for merge sort - splits the array
// and call merge function to sort and merge the array
// mergesort is a recursive function
static void mergesort(int Array[], int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
mergesort(Array, left, mid);
mergesort(Array, mid+1, right);
merge(Array, left, mid, right);
}
}
// merge function performs sort and merge operations
// for mergesort function
static void merge(int Array[], int left, int mid, int right) {
// Create two temporary array to hold split
// elements of main array
int n1 = mid - left + 1; //no of elements in LeftArray
int n2 = right - mid; //no of elements in RightArray
int LeftArray[n1], RightArray[n2];
for(int i=0; i < n1; i++) {
LeftArray[i] = Array[left + i];
}
for(int i=0; i < n2; i++) {
RightArray[i] = Array[mid + i + 1];
}
// In below section x, y and z represents index number
// of LeftArray, RightArray and Array respectively
int x=0, y=0, z=left;
while(x < n1 && y < n2) {
if(LeftArray[x] < RightArray[y]) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
}
else {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
}
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of LeftArray
while(x < n1) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of RightArray
while(y < n2) {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
z++;
}
}
// function to print array
static void PrintArray(int Array[], int n) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cout<<Array[i]<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}
// test the code
int main (){
int MyArray[] = {10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4};
int n = sizeof(MyArray) / sizeof(MyArray[0]);
cout<<"Original Array\n";
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
mergesort(MyArray, 0, n-1);
cout<<"\nSorted Array\n";
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
return 0;
}
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
#include <stdio.h>
static void mergesort(int Array[], int left, int right);
static void merge(int Array[], int left, int mid, int right);
static void PrintArray(int Array[], int n);
// function for merge sort - splits the array
// and call merge function to sort and merge the array
// mergesort is a recursive function
static void mergesort(int Array[], int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
mergesort(Array, left, mid);
mergesort(Array, mid+1, right);
merge(Array, left, mid, right);
}
}
// merge function performs sort and merge operations
// for mergesort function
static void merge(int Array[], int left, int mid, int right) {
// Create two temporary array to hold split
// elements of main array
int n1 = mid - left + 1; //no of elements in LeftArray
int n2 = right - mid; //no of elements in RightArray
int LeftArray[n1], RightArray[n2];
for(int i=0; i < n1; i++) {
LeftArray[i] = Array[left + i];
}
for(int i=0; i < n2; i++) {
RightArray[i] = Array[mid + i + 1];
}
// In below section x, y and z represents index number
// of LeftArray, RightArray and Array respectively
int x=0, y=0, z=left;
while(x < n1 && y < n2) {
if(LeftArray[x] < RightArray[y]) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
}
else {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
}
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of LeftArray
while(x < n1) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of RightArray
while(y < n2) {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
z++;
}
}
// function to print array
static void PrintArray(int Array[], int n) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
printf("%i ",Array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// test the code
int main (){
int MyArray[] = {10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4};
int n = sizeof(MyArray) / sizeof(MyArray[0]);
printf("Original Array\n");
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
mergesort(MyArray, 0, n-1);
printf("\nSorted Array\n");
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
return 0;
}
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
using System;
class MyProgram {
// function for merge sort - splits the array
// and call merge function to sort and merge the array
// mergesort is a recursive function
static void mergesort(int[] Array, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left)/2;
mergesort(Array, left, mid);
mergesort(Array, mid+1, right);
merge(Array, left, mid, right);
}
}
// merge function performs sort and merge operations
// for mergesort function
static void merge(int[] Array, int left, int mid, int right) {
// Create two temporary array to hold split
// elements of main array
int n1 = mid - left + 1; //no of elements in LeftArray
int n2 = right - mid; //no of elements in RightArray
int[] LeftArray = new int [n1];
int[] RightArray = new int [n2];
for(int i=0; i < n1; i++) {
LeftArray[i] = Array[left + i];
}
for(int i=0; i < n2; i++) {
RightArray[i] = Array[mid + i + 1];
}
// In below section x, y and z represents index number
// of LeftArray, RightArray and Array respectively
int x=0, y=0, z=left;
while(x < n1 && y < n2) {
if(LeftArray[x] < RightArray[y]) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
}
else {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
}
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of LeftArray
while(x < n1) {
Array[z] = LeftArray[x];
x++;
z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of RightArray
while(y < n2) {
Array[z] = RightArray[y];
y++;
z++;
}
}
// function to print array
static void PrintArray(int[] Array) {
int n = Array.Length;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
Console.Write(Array[i] + " ");
Console.Write("\n");
}
// test the code
static void Main(string[] args) {
int[] MyArray = {10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4};
int n = MyArray.Length;
Console.Write("Original Array\n");
PrintArray(MyArray);
mergesort(MyArray, 0, n-1);
Console.Write("\nSorted Array\n");
PrintArray(MyArray);
}
}
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
<?php
// function for merge sort - splits the array
// and call merge function to sort and merge the array
// mergesort is a recursive function
function mergesort(&$Array, $left, $right) {
if ($left < $right) {
$mid = $left + (int)(($right - $left)/2);
mergesort($Array, $left, $mid);
mergesort($Array, $mid+1, $right);
merge($Array, $left, $mid, $right);
}
}
// merge function performs sort and merge operations
// for mergesort function
function merge(&$Array, $left, $mid, $right) {
// Create two temporary array to hold split
// elements of main array
$n1 = $mid - $left + 1; //no of elements in LeftArray
$n2 = $right - $mid; //no of elements in RightArray
$LeftArray = array_fill(0, $n1, 0);
$RightArray = array_fill(0, $n2, 0);
for($i=0; $i < $n1; $i++) {
$LeftArray[$i] = $Array[$left + $i];
}
for($i=0; $i < $n2; $i++) {
$RightArray[$i] = $Array[$mid + $i + 1];
}
// In below section x, y and z represents index number
// of LeftArray, RightArray and Array respectively
$x=0; $y=0; $z=$left;
while($x < $n1 && $y < $n2) {
if($LeftArray[$x] < $RightArray[$y]) {
$Array[$z] = $LeftArray[$x];
$x++;
}
else {
$Array[$z] = $RightArray[$y];
$y++;
}
$z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of LeftArray
while($x < $n1) {
$Array[$z] = $LeftArray[$x];
$x++;
$z++;
}
// Copying the remaining elements of RightArray
while($y < $n2) {
$Array[$z] = $RightArray[$y];
$y++;
$z++;
}
}
// function to print array
function PrintArray($Array, $n) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $Array[$i]." ";
echo "\n";
}
// test the code
$MyArray = array(10, 1, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4);
$n = sizeof($MyArray);
echo "Original Array\n";
PrintArray($MyArray, $n);
mergesort($MyArray, 0, $n-1);
echo "\nSorted Array\n";
PrintArray($MyArray, $n);
?>
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 10 1 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
Time Complexity:
In all cases (worst, average and best), merge sort always divides the array until all sub-arrays contains single element and takes linear time to merge those sub-arrays. Dividing process has time complexity Θ(logN) and merging process has time complexity Θ(N). Therefore, in all cases, the time complexity of merge sort is Θ(NlogN).


