Stack in Java
A stack is a linear dynamic data structure that follows Last-In/First-Out (LIFO) principle. In a stack, addition of a new element and deletion of an element occurs at the same end which implies that the element which is added last in the stack will be the first to be removed from the stack.
Features of stack
- It is a dynamic data structure.
- It has dynamic size.
- It uses dynamic memory allocation.
Operations of a stack
- isEmpty(): Checks whether the stack is empty or not.
- size(): Returns the size of the stack.
- topElement(): Returns the top element of the stack.
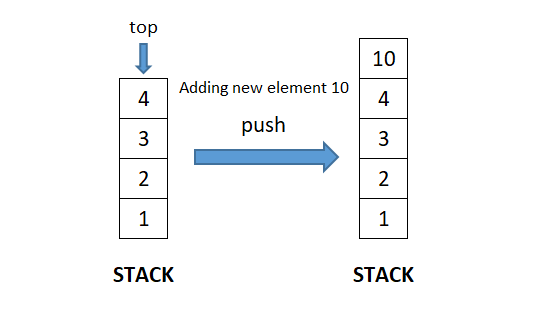
- push(x): Adds a new element ‘x’ at the top of the stack. Consequently, size of the stack increases by 1.
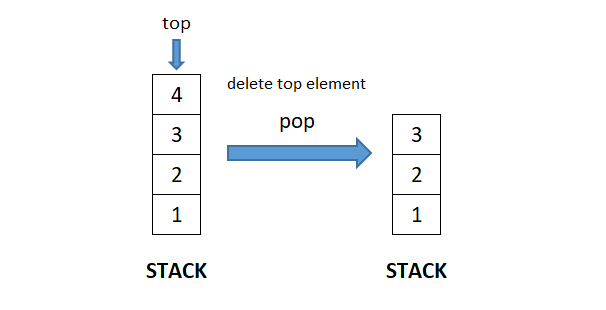
- pop(): Deletes the top element of the stack. Consequently, size of the stack decreases by 1.
Implementation of Stack
class CreateStack {
static final int MAX = 100;
int top;
//assigning MAX size of the stack
int stack[] = new int[MAX];
CreateStack() {
top = -1;
}
// create a method to check whether
// the stack is empty or not
void isEmpty() {
if(top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is not empty.");
}
}
//create a method to return size of the stack
int size() {
return top+1;
}
//create a method to add new element
void push(int x){
if(top == (MAX - 1)){
System.out.println("Stack size limit reached.");
} else {
stack[++top] = x;
System.out.println(x + " is added into the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to delete top element
void pop(){
if(top < 0){
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
} else {
int x = stack[top--];
System.out.println(x + " is deleted from the stack.");
}
}
//create a method to get top element
int topElement() {
if(top < 0) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
return 0;
} else {
return stack[top];
}
}
}
// test the code
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CreateStack MyStack = new CreateStack();
MyStack.push(10);
MyStack.push(20);
MyStack.push(30);
MyStack.push(40);
MyStack.pop();
MyStack.isEmpty();
}
}
The above code will give the following output:
10 is added into the stack. 20 is added into the stack. 30 is added into the stack. 40 is added into the stack. 40 is deleted from the stack. Stack is not empty.
Recommended Pages
- Java Program - To Check Prime Number
- Java Program - Bubble Sort
- Java Program - Selection Sort
- Java Program - Maximum Subarray Sum
- Java Program - Reverse digits of a given Integer
- Java - Swap two numbers
- Java Program - Fibonacci Sequence
- Java Program - Insertion Sort
- Java Program - Find Factorial of a Number
- Java Program - Find HCF of Two Numbers
- Java Program - To Check Whether a Number is Palindrome or Not
- Java Program - To Check Whether a String is Palindrome or Not
- Java Program - Heap Sort
- Java Program - Quick Sort
- Java - Swap Two Numbers without using Temporary Variable
- Java Program - To Check Armstrong Number
- Java Program - Counting Sort
- Java Program - Radix Sort
- Java Program - Find Largest Number among Three Numbers
- Java Program - Print Floyd's Triangle