C++ - If-Else Statements
If Statement
The If statement is used to execute a block of code when the condition is evaluated to be true. When the condition is evaluated to be false, the program will skip the if-code block.
Syntax
if(condition){
statements;
}
Flow Diagram:
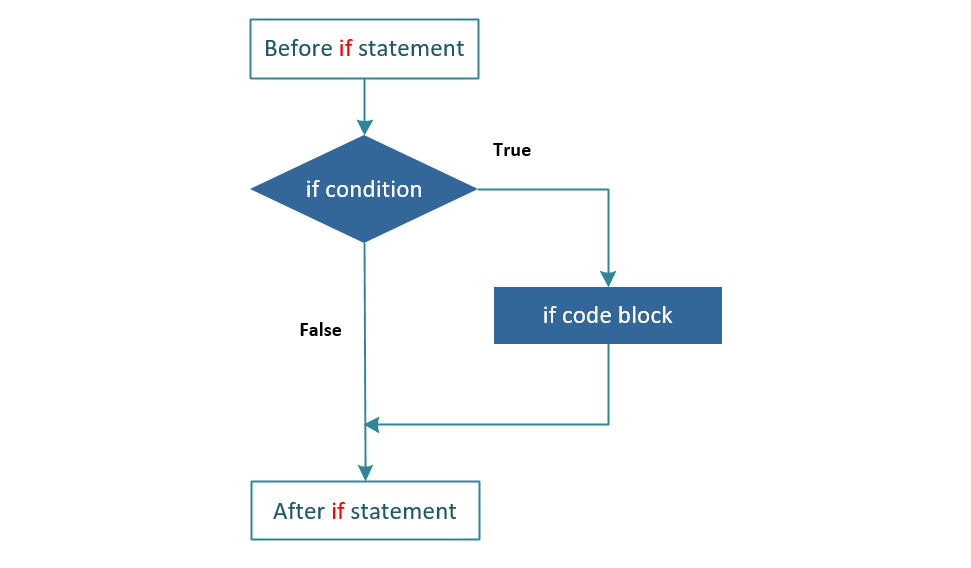
In the example below, the if code block is created which executes only when the variable called i is divisible by 3.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int i = 15;
if (i % 3 == 0){
cout<<i<<" is divisible by 3.";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
15 is divisible by 3.
If-else Statement
The else statement is always used with if statement. It is used to execute block of codes whenever if condition gives false result.
Syntax
if(condition){
statements;
} else {
statements;
}
Flow Diagram:
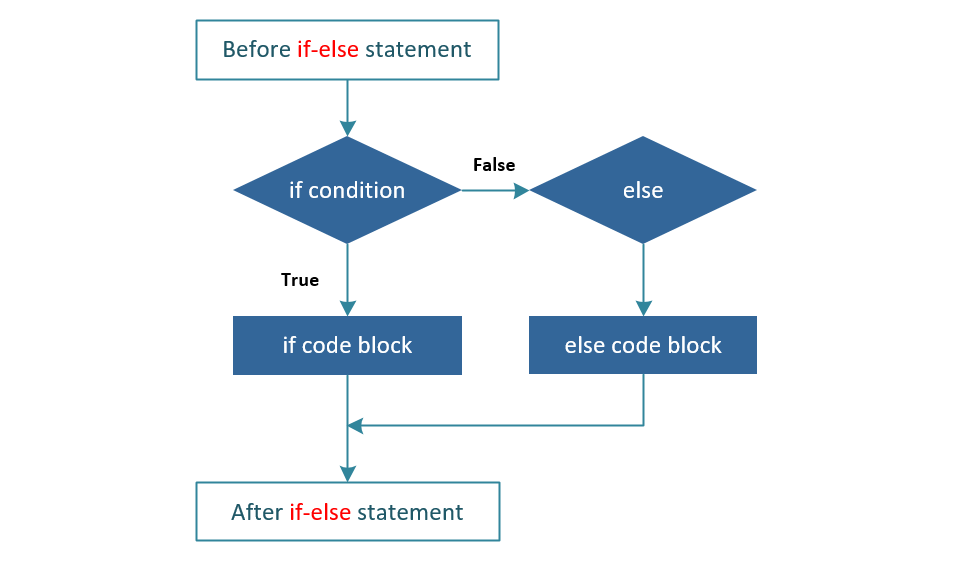
In the example below, else statement is used to print a message if the variable i is not divisible by 3.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
int i = 16;
if (i % 3 == 0) {
cout<<i<<" is divisible by 3.";
} else {
cout<<i<<" is not divisible by 3.";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
16 is not divisible by 3.
else if Statement
For adding more conditions, else if statement in used. The program first checks if condition. When found false, it checks else if conditions. If all else if conditions are found false, then else code block is executed.
Syntax
if(condition){
statements;
} else if(condition) {
statements;
}
...
...
...
} else {
statements;
}
Flow Diagram:
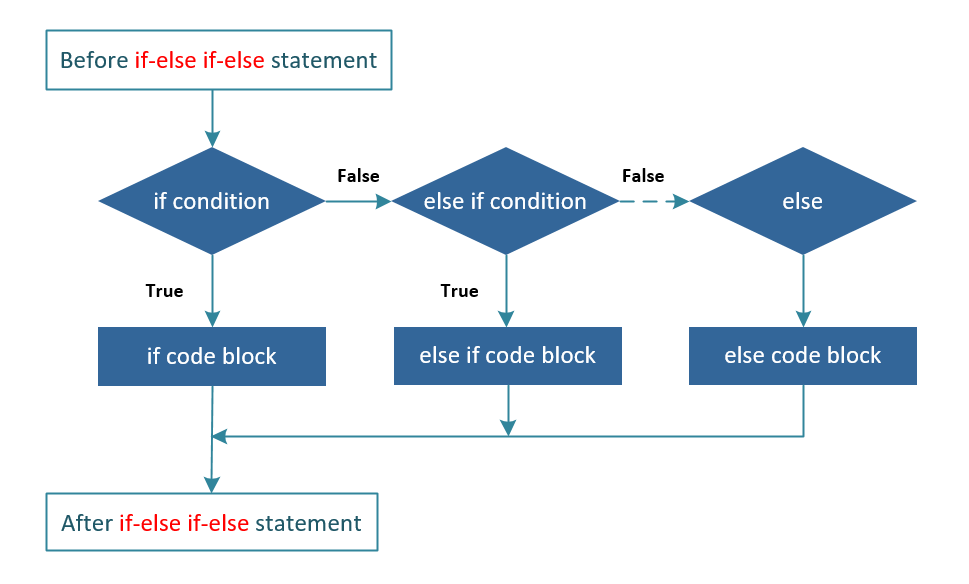
In the example below, else if statement is used to add more conditions between if statement and else statement.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int i = 16;
if (i > 25) {
cout<<i<<" is greater than 25.\n";
} else if(i <=25 && i >=10) {
cout<<i<<" lies between 10 and 25.\n";
} else {
cout<<i<<" is less than 10.\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
16 lies between 10 and 25.


