C++ - Switch
The Switch statement in C++ language is used to execute one of many code statements. It can be considered as group of If-else statements.
Syntax
switch (expression){
case 1:
statement 1;
break;
case 2:
statement 2;
break;
...
...
...
case N:
statement N;
break;
default:
default statement;
}
The Switch expression is evaluated and matched with the cases. When Case matches, the following block of code is executed.
Flow Diagram:
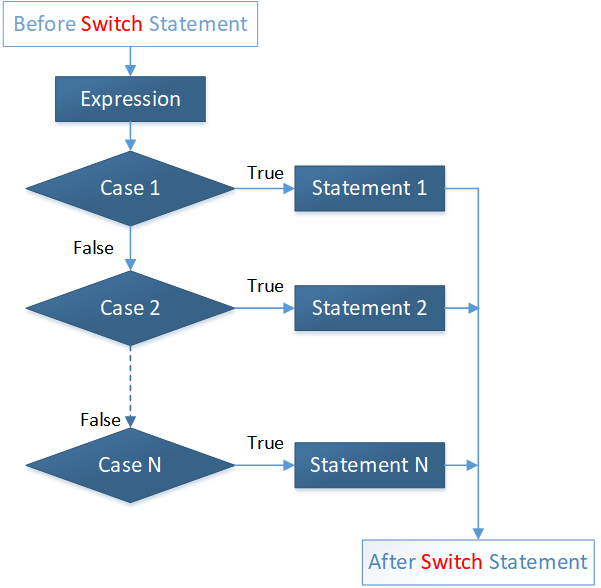
Example:
In the example below, the switch expression is a variable called i with value 2 which is matched against case values. When the case value matches with expression value, the following block of code is executed.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
int i = 2;
switch(i){
case 1:
cout<<"Red\n";
break;
case 2:
cout<<"Blue\n";
break;
case 3:
cout<<"Green\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
Blue
default and break statements
Default case and break statement are optional here.
- Default Case: Default Statement is executed when there is no match between switch expression and test cases.
- Break Statement: Break statement is used to get out of the Switch statement after a match is found.
Example:
In the example below, the switch expression is a variable called i with value 10 which is matched against case values. As there is no case that matches with value 10, hence default block of code gets executed.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
int i = 10;
switch(i){
case 1:
cout<<"Red\n";
break;
case 2:
cout<<"Blue\n";
break;
case 3:
cout<<"Green\n";
break;
default:
cout<<"No match found.\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
No match found.
Please note that, the default statement can be placed at any position in the switch statement. In such instances, add break statement with default statement.
Example:
Consider the example below, where default statement is placed on the top in a switch statement.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
int i = 10;
switch(i){
default:
cout<<"No match found.\n";
break;
case 1:
cout<<"Red\n";
break;
case 2:
cout<<"Blue\n";
break;
case 3:
cout<<"Green\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
No match found.
Common code blocks
There are instances where same code block is required in multiple cases.
Example:
In the example below, same code block is shared for different switch cases.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
int i = 10;
switch(i){
case 1:
cout<<"Red\n";
break;
case 2:
case 10:
cout<<"Blue\n";
break;
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
cout<<"Green\n";
}
return 0;
}
The output of the above code will be:
Blue


