C++ Program - Bubble Sort
Bubble sort is the simplest sorting algorithm. The Bubble sort is based on the idea that every adjacent elements are compared and swapped if found in wrong order.
Example:
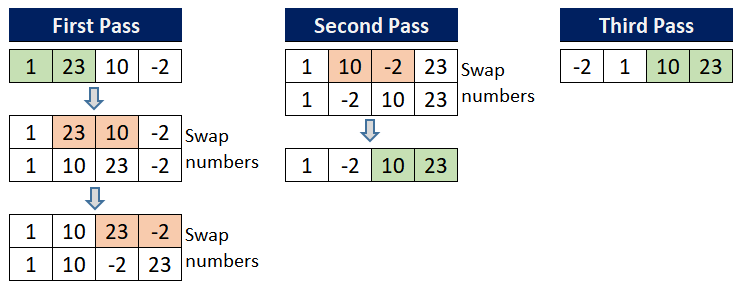
To understand the bubble sort, lets consider an unsorted array [1, 23, 10, -2] and discuss each step taken to sort the array in ascending order. In every pass, two adjacent elements are checked and swapped if found in wrong order.
First Pass: (1) and (23) are compared and found in correct order(ascending order in this case). After that (23) and (10) are compared, since (23>10), hence these numbers are swapped. Then (23) and (-2) are compared and swapped.
Second Pass: (1) and (10) are compared and found in correct order. Then (10) and (-2) are compared, since (10>-2), hence these numbers are swapped. After that (10) and (23) are compared and found in correct order.
Third Pass: (1) and (-2) are compared, since (1>-2), hence these numbers are swapped. After that (1,10) and (10,23) are checked and found in correct order.
Implementation of Bubble Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function for bubble sort
static void bubblesort(int Array[], int n) {
int temp;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<n-i-1; j++) {
if(Array[j]>Array[j+1]) {
temp = Array[j];
Array[j] = Array[j+1];
Array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// function to print array
static void PrintArray(int Array[], int n) {
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
cout<<Array[i]<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}
// test the code
int main (){
int MyArray[] = {1, 10, 23, 50, 4, 9, -4};
int n = sizeof(MyArray) / sizeof(MyArray[0]);
cout<<"Original Array\n";
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
bubblesort(MyArray, n);
cout<<"\nSorted Array\n";
PrintArray(MyArray, n);
return 0;
}
The above code will give the following output:
Original Array 1 10 23 50 4 9 -4 Sorted Array -4 1 4 9 10 23 50
Time Complexity:
The time complexity of bubble sort is Θ(N²) in all cases even if the whole array is sorted because the entire array need to be iterated for every element and it contains two nested loops.
Recommended Pages
- C++ - Swap two numbers
- C++ Program - Fibonacci Sequence
- C++ Program - Insertion Sort
- C++ Program - Find Factorial of a Number
- C++ Program - Find HCF of Two Numbers
- C++ Program - Merge Sort
- C++ Program - Shell Sort
- Stack in C++
- Queue in C++
- C++ Program - Find LCM of Two Numbers
- C++ Program - To Check Whether a Number is Palindrome or Not
- C++ Program - To Check Whether a String is Palindrome or Not
- C++ Program - Heap Sort
- C++ Program - Quick Sort
- C++ - Swap Two Numbers without using Temporary Variable
- C++ Program - To Check Armstrong Number
- C++ Program - Counting Sort
- C++ Program - Radix Sort
- C++ Program - Find Largest Number among Three Numbers
- C++ Program - Print Floyd's Triangle


