NumPy - Linear Algebra
The NumPy package contains a number of functions which provides all the functionality required for linear algebra. Below mentioned are the most frequently used functions to perform different algebraic calculations.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| dot() | Return dot product of two arrays. |
| vdot() | Return dot product of two vectors. |
| inner() | Return inner product of two arrays. |
| matmul() | Return matrix multiplication of two arrays. |
| det() | Calculate the determinant of a matrix. |
| solve() | Solves the linear matrix equation. |
| inv() | Return multiplicative inverse of the matrix. |
Lets discuss these functions in detail:
numpy.dot() function
The numpy.dot() function returns the dot product of two arrays. In the example below, dot product of Arr1 and Arr2 is calculated.
import numpy as np
Arr1 = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
Arr2 = np.array([[10, 20],
[30, 40]])
Arr3 = np.dot(Arr1, Arr2)
print(Arr3)
The output of the above code will be:
[[ 70 100] [150 220]]
The dot product is calculated as:
[[1*10+2*30 1*20+2*40] [3*10+4*30 3*20+4*40]] = [[ 70 100] [150 220]]
numpy.vdot() function
The numpy.vdot() function returns the dot product of two vectors. In the example below, dot product of vec1 and vec2 is calculated.
import numpy as np vec1 = np.array([1, 2, 3]) vec2 = np.array([10, 20, 30]) retval = np.dot(vec1, vec2) print(retval)
The output of the above code will be:
140
The dot product is calculated as:
1*10+2*20+3*30 = 140
numpy.inner() function
The numpy.inner() function returns the inner product of two arrays. In the example below, inner product of Arr1 and Arr2 is calculated.
import numpy as np
Arr1 = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
Arr2 = np.array([[10, 20],
[30, 40]])
Arr3 = np.inner(Arr1, Arr2)
print(Arr3)
The output of the above code will be:
[[ 50 110] [110 250]]
The inner product is calculated as:
[[1*10+2*20 1*30+2*40] [3*10+4*20 3*30+4*40]] = [[ 50 110] [110 250]]
numpy.matmul() function
The numpy.matmul() function is used to calculate the matrix multiplication of two arrays. In the example below, matrix multiplication of Arr1 and Arr2 is calculated.
import numpy as np
Arr1 = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
Arr2 = np.array([[10, 20],
[30, 40]])
Arr3 = np.matmul(Arr1, Arr2)
print(Arr3)
The output of the above code will be:
[[ 70 100] [150 220]]
The matrix multiplication is calculated as:
[[1*10+2*30 1*20+2*40] [3*10+4*30 3*20+4*40]] = [[ 70 100] [150 220]]
numpy.linalg.det() function
The numpy.linalg.det() function is used to calculate determinant of a matrix. In the example below, determinant of matrix mat is calculated.
import numpy as np
mat = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
retval = np.linalg.det(mat)
print(retval)
The output of the above code will be:
-2.0000000000000004
The determinant is calculated as:
1*4-2*3 = -2
numpy.linalg.solve() function
The numpy.linalg.solve() function is used to solve the linear matrix equation. Consider the below mentioned system of linear equations:
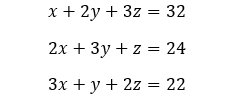
Which can be represented as below in the matrix form.
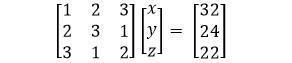
The solution of the above equations is: x=1, y=5, z=7. This can be solved using numpy.linalg.solve() function as shown in the example below.
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 1],
[3, 1, 2]])
B = np.array([32, 24, 22])
sol = np.linalg.solve(A, B)
print(sol)
The output of the above code will be:
[ 1. 5. 7.]
numpy.linalg.inv() function
The numpy.linalg.inv() function is used to calculate the multiplicative inverse of the given matrix. In the example below, multiplicative inverse of matrix mat is calculated.
import numpy as np
mat = np.array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
invmat = np.linalg.inv(mat)
print("Original matrix:")
print(mat)
print("\nInverse matrix:")
print(invmat)
The output of the above code will be:
Original matrix: [[1 2] [3 4]] Inverse matrix: [[-2. 1. ] [ 1.5 -0.5]]


